
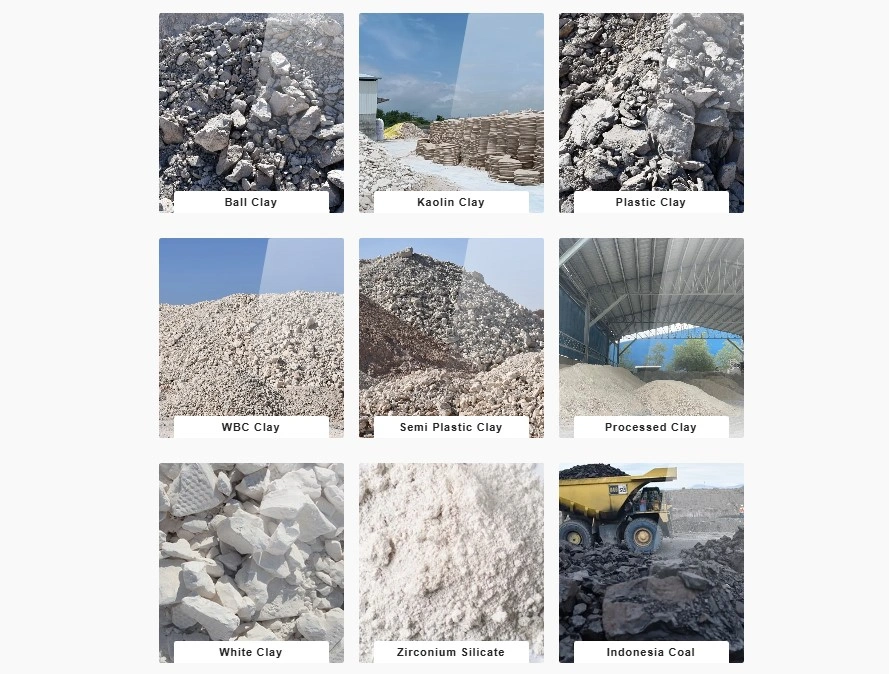
Types of Clay Used in Ceramic Industry
03 March, 2026
01 February, 2025
Clay minerals find application in almost every industry with ceramic products, construction and pharmaceutics industries, cosmetic products industries being some of the major users. Kaolin, bentonite and ball clay are white and naturally occurring and have properties that are distinct and make them useful in various industries. However, do you ever think about the processing of industrial clay minerals to fit into all these requirements?
In this blog, we will discover the main stages regarding the industrial clay minerals processing and the facets affecting its applicability.
Industrial clay minerals are fine-grained minerals mainly consisting of hydrous aluminum silicates. The naturally occurring clays are characterized by desirable properties such as plasticity, cohesiveness and water retention abilities hence their usability. Below are some key types of industrial clay minerals:

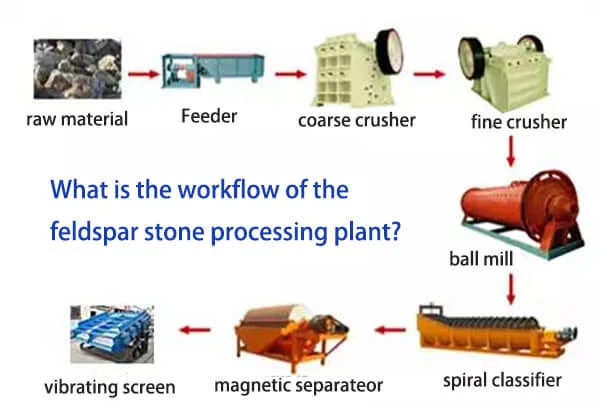
The first process in the utilization of industrial clay minerals is mining or extraction of the product. Clay is often mined from open cast mines as the clay is removed from the ground with earth moving machines. The clay is grouped and in many cases layers of the clay can be distinguished while the type of clay depends with the region. Once the specific clay mineral has been determined, the resource is selectively mined and then transloaded to higher order processing. The process typically involves:
Removal of Overburden: The overburden, which is a layer of soil and rock above the clay deposit, isleared with shovels and scraper machines.
Extraction: When overburden has been removed, clay is then excavated either by hand along the edges with spades and forks or by dragline.
After extraction, the clay minerals are usually further processed by crushing and grinding to make it easier to handle. This step is crucial for reducing the size of the clay beforehand and thereby making it easier for further processing. Screens and classifiers are used to obtain the required size of the particles that are important for the final product quality and its application.
Crushing: Blunt masses of clay are then introduced into breakers that further reduce them into smaller bits.
Grinding: The crushed clay is then ground to fine powder using a mill. This step may use wet or dry grinding it all depending on the desired character of the final product.
Innovative clay online has a lot of negative characteristics such as containing sand, silt or even iron oxide which influences their quality and color. Such materials have to be washed and purified in order to eliminate them. The clay is generally cleaned with water or other chemicals to enhance the clarion brightness, purity and pliantly or plasticity or degree of mouldability. This is especially the case with products such as kaolin where color quality and brightness serves the industries that uses it most especially in paper manufacturing and ceramics.
Subsequently, the clay is dried to eliminate any forms of moisture after the washing process has been completed. This is often accomplished in rotary dryers or an air-drying system depending on the form of the clay and the floe of the final end product. Drying remove water from the livestock, crops or fish in a level that can enhance storage, transport and other value addition processes.
Air Drying: The process of evaporation under normal conditions and under controlled environment.
Mechanical Drying: Forcing out or evaporating moisture by employing tools including rotary dryers or any other efficient equipment.
On the other hand, after the clay is dried, the tested sample is categorized by the size of its particles and other characteristics. This step often involves:
Screening: It is sifted through a screen separating out very fine particles from bigger sizes of the clay.
Hydraulic Classification: At times, people have been able to use water to sort particles depending on their relative density.
In other cases, the clay minerals are made to go through some chemical processing to make them acquire certain characteristics. It may include uses of acid treatment or bleaching or the use of other chemicals to reduce the clay’s coarseness, alter its color or increase its viscosity. For instance, montmorillonite which is the main constituent of bentonite clay may be retreated with sodium or calcium so that it enhances the swelling characteristic to suit a purpose of using in drilling fluids.
Acid Activation: Acid treatment is used for the enhancement of the adsorption capacity of bentonite for application in industrial processes.
Flotation: It can be used to ‘wash’ the surface of kaolin clay or other clays with a solvent in order to release unwanted impurities due to variation in surface chemistry .
The last formed clay is packed in the right kind of packets depending on its usage. Regardless of the amount of the clay required for a particular industry or for individual consumer products, the packing accentuates the need to maintain the clay dry and free from the impurities that may be found in the natural environment. The clay is packaged depending on the demand of the industries then transported to its various users.
Calcination: Lime is a clay that is calcined to enhance its characteristics that fit certain uses for this commodity.
Blunging and Fractionation: Comprises combination with water forming a suspension that can be further treated through beneficiation processes.
Bagging and Loading: The last processing for this kind of material is packaging the final product ready for selling. This includes packing the clay in large bunches or small parcels as may suit a client.
Processed industrial clay minerals have a wide range of applications in different industries:
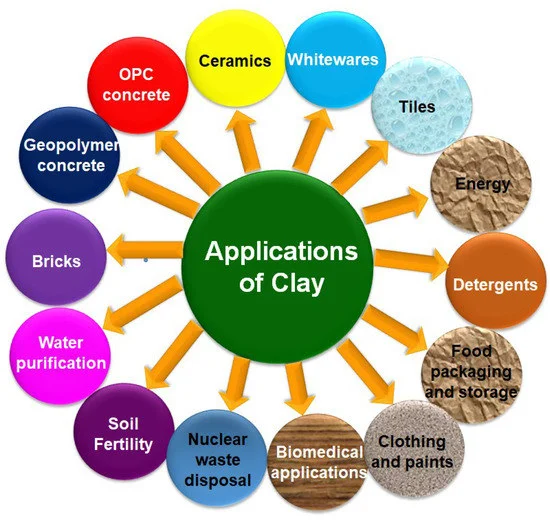
They include extraction of industrial clay minerals, crushing, washing of clay, drying, and at times an added chemical treatment. Every stage is crucial to guaranteeing the finished product meets the specifications of quality for the industry it will be used in. For ceramics, paper, constructions and even cosmetics, industrial mineral clay is so essential in those fields.
If you are in need of clay minerals to be used in your business then it is advisable that you select a supplier who will supply processed minerals for your business needs. For further information, please visit Jay Ganesh Minerals for more information on how our clay mineral solutions can help your business.

Whatsapp Chatx
Hi! Click one of our representatives below to chat on WhatsApp or send us email to [email protected]

|
Mr. RAJESH +91 99130 87000 |

|
Mr. JIGNESH +91 89800 70055 |

