
Types of Clay Used in Ceramic Industry
03 March, 2026
05 July, 2025
Kaolin clay (or china clay) is a naturally formed soft and white mineral which is highly valued due to its exclusive chemical and physical behavior. It is a purity determinant when applied in ceramics and paints, rubber, pharmaceutical and personal care products. Defective ceramic, low absorbency of cosmetics and failure to follow regulations of pharmaceuticals are some of the results of impure kaolin.
In the present guide, we will explain how you can follow the process step by step, whether by simple home tests or more sophisticated laboratories, both in order to make sure your material complies with the acceptable standards. Whether you're sourcing kaolin for ceramics or kaolin clay for skin, maintaining consistent quality is essential.
The purity of kaolin directly impacts its functionality, especially in industries where color, texture, or chemical composition affects end-use.

For example:
Ceramic manufacturers demand high-whiteness kaolin clay for smooth, bright glazes and bodies.
Cosmetic brands require low-metal content and smooth particle distribution to ensure gentle skincare formulations, especially in kaolin clay for skin and kaolin clay for hair products.
Paper coating applications need pure kaolin to enhance printability and gloss without discoloration.
Pharmaceutical and food-grade kaolin must undergo high levels of safety standards, which include zero levels of undesired heavy metal contamination as well as zero levels of microbes.
Consequently, the level of impurity ought to be constantly monitored to keep the products of any industry reliable, consumers safe and comply with regulations. Monitoring also helps control kaolin price fluctuations caused by quality inconsistency.
kaolinite deposits naturally contain a variety of contaminants that reduce their industrial value if not removed or controlled. Some common impurities include:
| Impurity Type | Impact on Use | Detection Method |
| Iron Oxides | Causes yellow, red, or brown discoloration; lowers brightness | Visual inspection, X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) |
| Titanium Oxides | Reduces whiteness, may alter electrical properties | XRF, spectrophotometry |
| Quartz (Silica) | Increases abrasiveness, affects texture in ceramics | X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), sedimentation |
| Organic Matter | Causes odor, microbial growth, dark specks in firing | Loss on Ignition (LOI), microbial culture |
| Heavy Metals | Toxic in food, pharma, cosmetics; regulatory issue | ICP-MS, AAS (Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy) |
| pH Irregularity | May irritate skin or disrupt chemical processes | pH testing kits, electronic pH meter |
Start your testing with a simple visual and tactile inspection, which can instantly reveal gross impurities:

Color Check: The presence of any trace of yellow, grey, and red color indicates iron or titanium contamination, making it of low preciousness in the high-grade properties.
Texture & Touch Test: Rub between the fingers a pinch of dry kaolin powder. Kaolin of high purity must be smooth, silky and soft. Coarse particles are likely to contain sand, quartz, or rough minerals.
Odor Inspection: Smell the clay. It should not have a specific smell or, at most, only a faint earthy smell. Any musty, metallic, or chemical smell should indicate an organic impurity or microbial contamination.
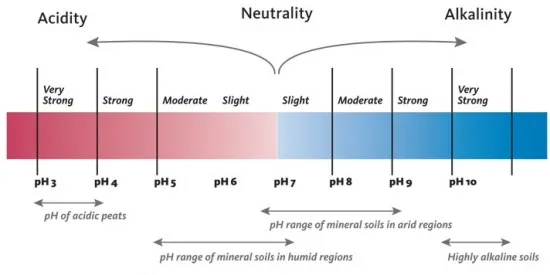
The pH level of kaolin clay slurry provides critical insight into its surface chemistry, essential for cosmetic, coating, and medical uses.
Procedure:
Mix 10 grams of kaolin powder with 100 ml of distilled water in a clean container.
Stir well and let it stand for 10–15 minutes.
Dip a pH strip or electrode probe into the water (not the settled clay).
Ideal Range: 6.5 to 8.5.
A pH below 6 could indicate acidic organic residues or mineral sulfides.
A pH above 8.5 suggests possible contamination with alkaline salts or limestone.
A balanced pH ensures chemical stability for applications in kaolin clay for skin, pharmaceuticals, and industrial fillers.
Sedimentation testing assists in identifying the presence of an excess of coarse materials such as quartz, feldspar, or sand, which are not suitable for fine use.
Procedure:
Add 5 grams of kaolin into a transparent glass jar with 200 ml of distilled water.
Shake vigorously for 1–2 minutes.
Let the mixture settle, noting the clarity of water and time required for particles to descend.
Pure white kaolin clay forms a smooth, stable suspension with fine particles settling very slowly.
Mad rapid settling or cloudiness caused by the presence of gritty layers are the sign of contamination by coarse minerals or quartz, which lowers value in high-tech ceramics or paper coatings.
Though home testing kits are available, laboratory tests are required to reveal pernicious heavy metals such as lead, arsenic, cadmium, or mercury.
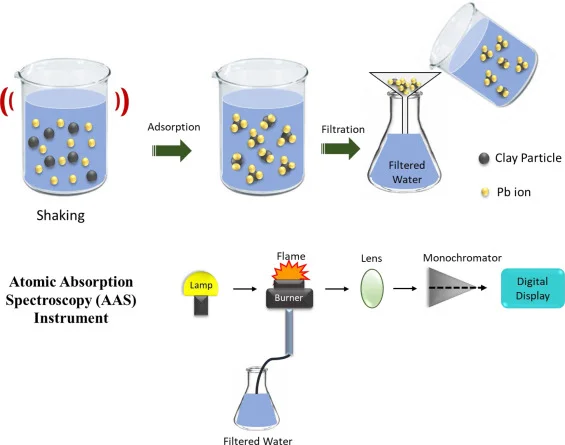
The gold standard, providing a means of detecting toxic elements in an ultra-trace manner, is ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry).
To detect in a simple qualitative fashion, silver nitrate paper, or Sodium sulfide paper, can be used to give a visible result when ions such as chlorides or sulfides are present, though these methods are not quantitative or specific.
Such extracted tests make kaolin clay appropriate in pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food-contact uses, where the restrictions on impurities are strict. Testing also helps in determining fair kaolin price based on its suitability for sensitive applications.
LOI tests estimate moisture, organic matter, and volatile compound content, important indicators of kaolin purity.

Procedure:
Weigh a clean ceramic crucible (W1).
Add 2 grams of kaolin (W2), weigh again.
Heat the crucible to 550°C for 1 hour to burn off organics and water.
Cool and weigh again (W3).
LOI (%) = ((W2 – W3) ÷ W2) × 100%
High-quality kaolin powder shows LOI below 10%.
High LOI suggests organic contamination or excessive bound water, which can cause defects in fired ceramics or reduce filler performance.
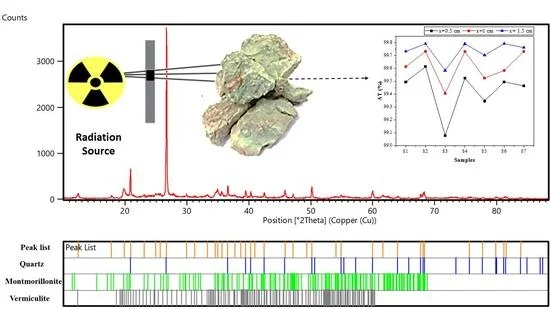
For precision-demanding industries:
XRD (X-Ray Diffraction): Properly measures crystalline impurities like quartz, mica or feldspar.
FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy): Identifies the chemical bonds and tiny organic compounds.
UV-Vis Spectrophotometry: Determines colored contaminants such as iron or titanium oxides that have an impact on brightness.
These advanced lab methods verify the mineralogical purity of kaolin clay, which is vital to use in ceramics, paints and in electronics. They also help demonstrate the benefit of kaolin clay in delivering consistent quality.
For kaolin clay used in cosmetics, medicines, or food packaging, microbial purity is critical:
TVC (Total Viable Count): Detects bacteria and fungi.
Pathogen Testing: Screens for harmful microbes like Salmonella, Staphylococcus aureus, or E. coli.
Recognition of ISO, ISO9001, ISO 22000 or cGMP or any other international certification provides traceability, quality assurance, and regulatory compliance, which enhances the trust in the market.
Use multiple batches to verify consistency.
Store samples in airtight, contamination-free containers.
Record every result; this will help in traceability and process improvement.
Prefer lab-certified tests if kaolin is meant for sensitive or regulated applications.
When sourcing kaolin or other industrial minerals, Jay Ganesh Minerals stands out as a trusted manufacturer and supplier of industrial fuels and mineral products, including high-grade kaolin clay bulk. The high standards of quality testing and the unwavering quality of purity and well-established supply chains ensure that all their minerals are of the industry standards, both in national and international markets. Jay Ganesh Minerals is the best source of quality industrial-grade kaolin and other vital minerals in the market because it has well-developed processing factories and emphasizes sustainability.
The purity of kaolin clay has a direct impact on the functionality, appearance, and security within a number of industries. Using a mixture of visual, chemical and instrumental tests, it is possible to confidently ascertain the quality of kaolin clay of specified use (ceramics, cosmetics, the pharmaceutical field, construction materials, etc.
Periodic testing and use of standard brands of suppliers such as Jay Ganesh Minerals ensures the long-term integrity and the safety as well as efficiency of your kaolin powder, safeguarding your brand name and consumers. Understanding the benefit of kaolin clay and sourcing responsibly ensures long-term success across all industries that rely on this versatile mineral.

Whatsapp Chatx
Hi! Click one of our representatives below to chat on WhatsApp or send us email to [email protected]

|
Mr. RAJESH +91 99130 87000 |

|
Mr. JIGNESH +91 89800 70055 |

