Introduction to Industrial Fuels & Coal
Different industrial sectors depend on industrial fuels to operate their power systems within manufacturing industries and transportation networks and energy production facilities. Coal stands as one of the most extensively used ancient energy resources which supports power generation along with steel production and cement operations. The following section examines industrial fuel definitions along with coal's essential value and details the mining and refining and processing procedures.
The production of energy through industrial applications requires industrial fuels as particular substances. Coal, natural gas and petroleum products including diesel and gasoline represent the different states of industrial fuels.
Importance of Coal in Industries

The different industries use coal as their main energy supply through these sectors:
- Power generation is used in coal-fired power plants.
- Steel production makes use of metallurgical coke for its production.
- The heat produced in kilns receives assistance from cement manufacturing operations.
- The chemical industry depends on coal to create synthetic fuels together with multiple chemical products
Multiple industrial procedures which include coal mining and processing and refining together support efficient coal usage and decreased ecological effects
Overview of Mining, Refining, and Processing
The production chain of coal starts from mining and continues through refinement until processing steps finish. Coal mining recovers underground coal deposits after processing transforms coal through cleaning followed by washing before it becomes usable in the form of coke or synthetic fuels.
Types of Coal and Their Uses
Different types of coal are classified through carbon content assessment and energy output measurement for industrial applications. The discussion will address the characteristics together with industrial applications of Lignite Coal and Indonesia Coal.
Lignite Coal
Characteristics: Lignite stands as the most inferior coal grade because it possesses both reduced carbon composition and energy power values. The quantity of moisture within Lignite exceeds other coals without the same heating value strength.
Uses: Electricity generation remains the primary application of this resource because of its economical viability together with wide availability. This material finds usage in various industrial setups that focus on economical operations.
Indonesia Coal
Characteristics: People commonly recognize Indonesian coal because it contains high levels of moisture yet keeps low ash and sulfur quantities which promotes cleaner combustion.
Uses: The application of this coal type occurs in power plants together with industrial operations while specific regions need low-sulfur coal to satisfy environmental regulations.
Jay Ganesh Minerals is a trusted exporter of Lignite Coal and Indonesian Coal, providing high-quality industrial fuel with reliable supply and superior efficiency.

Uses of Different Coal Types in Industries
Different coal types are used in various industries based on their properties:
- Power Generation: Lignite and Indonesia coal are both used extensively in coal-fired power plants.
- Cement Industry: Lignite coal is commonly used due to its availability and affordability.
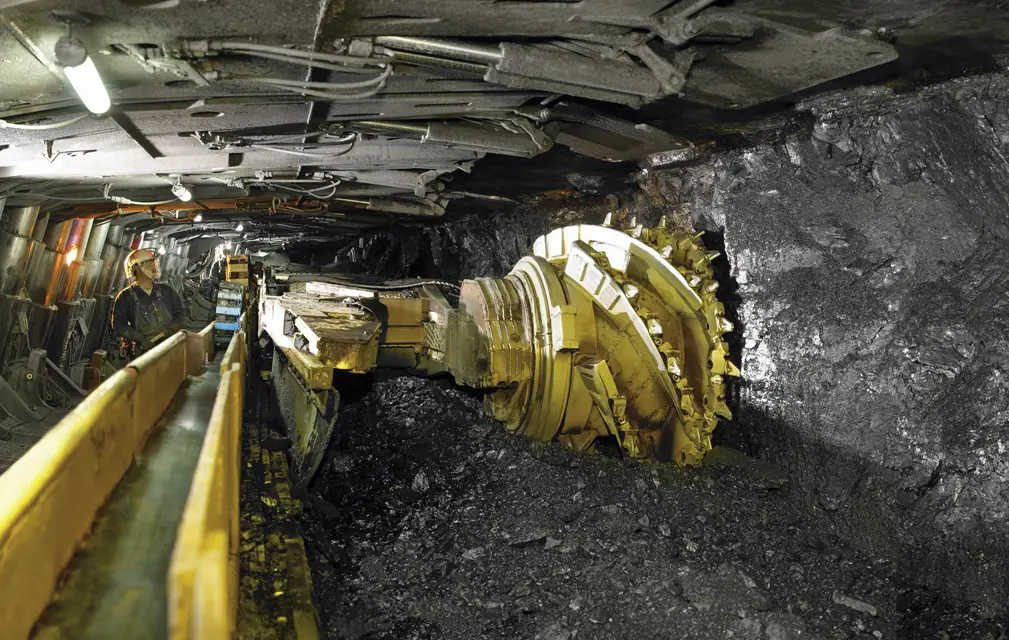
How Coal is Mined
Surface Mining Techniques
This type of mining becomes suitable when coal deposits exist relatively near to surface levels.
Strip Mining
- The process removes soil layers along with rock material from the surface one by one.
- Economical coal extraction occurs through the use of extensive equipment.
Open-Pit Mining
- An extensive digging operation produces pits to reach extensive coal layers at depth.
- More expensive but useful for certain reserves.
Underground Mining Methods
This mining method is employed when coal reservoirs extend deep beneath the surface.
Room-and-Pillar Mining
- The mine roof receives support from pillars of coal left in place.
- Common in areas with stable geological conditions.
Longwall Mining
- The automated equipment performs a continuous process of coal cutting.
- The system works effectively though specific preparation is essential to stop rocks from collapsing.

Geographical Distribution of Coal Reserves
Major Coal-Producing Countries
- China – Largest producer and consumer.
- India – Second-largest producer with growing demand.
- United States – Major exporter with abundant reserves.
- Australia – Large exporter of high-quality coal.
- Russia – Supplies coal to European and Asian markets.
Global Coal Reserves and Their Significance
- The worldwide coal reserves amount to an estimated total of 1.07 trillion tons.
- The usage of coal continues to persist as a primary energy source while the renewable sector grows.
Coal Refining and Processing Steps
Coal Cleaning and Washing
Businesses need to refine coal before putting it into industrial use because impurities must be removed.
Removing Impurities
- Improvement of combustion efficiency occurs through the removal of sulfur along with rock and soil.
- The procedure diminishes air contamination and decreases the amount of ash produced.
Techniques Used
- Dense medium separation functions as an operation which functions to separate coal from waste materials through density distinctions.
- A flotation process utilizes chemicals to achieve the removal of unwanted substances.
Coal Coking Process
- The production process changes raw coal into metals-processing coke which serves the steel industry.
- When heating coal without oxygen present manufacturers can produce Coke.
Gasification and Liquefaction
- Converts coal into synthetic gas (syngas) or liquid fuels.
- The production method yields diesel products and gasoline in addition to chemical substances.
Environmental Impact of Coal Mining and Processing
The extraction and refinement of coal generate major adverse effects on the environment.
Air Pollution from Coal Processing
- The combination of CO2 with SO2 and NOx emissions during coal burning causes both atmospheric pollution and climate warming damages.
- The release of coal pollution causes respiratory diseases and leads to various health problems.
Water Contamination Issues
- The production process of mining results in water pollution due to acid mine drainage.
- The risk of encountering health problems results from exposure to polluted water sources.
Land Degradation and Reclamation
- Land subsidence along with habitat destruction becomes an outcome of mining operations.
- Reclamation operations following mining consist of converting mined areas into natural ecosystems.
Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Coal Processing Methods
Clean Coal Technology
- The technology uses scrubbers with filters to minimize emissions release.
- Improves coal combustion efficiency.
Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
- This procedure captures emissions from CO₂ before they escape into the air.
- The storage takes place underground to minimize climate effect.
Recycling and Reuse of Byproducts
- The production of cement requires fly ash as a major ingredient.
- The production of chemicals along with road materials utilizes coal tar as an ingredient.
Coal and Power Generation
Role of Coal in Electricity Production
- Coal-powered electricity facilities produce approximately 35% of all global electricity.
- The system delivers steady and dependable electrical energy.
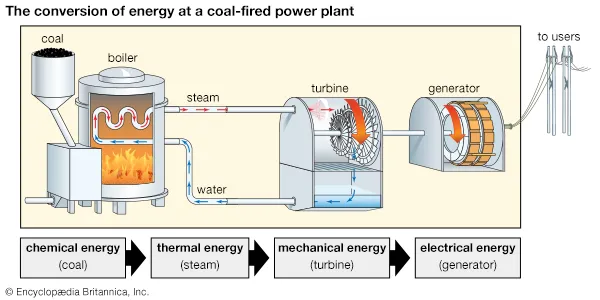
Coal-Fired Power Plants
- Heat production from coal burns while water turns into steam.
- The power turbine turns because it receives steam energy from generators.
Steam Turbines and Energy Conversion
- Converts thermal energy into mechanical energy.
- These units power traditional power plants and supercritical power plants to enhance performance.
Future of Coal in the Industrial Sector
Coal faces an uncertain future because environmental concerns combine with developing technological solutions.
Transition to Renewable Energy Sources
- The world is presently moving into a direction of exploiting renewable energy resources that include wind power and solar power generation.
- The necessity of coal remains crucial to maintain energy security throughout various parts of the world.
Role of Coal in the Energy Mix
- Coal continues to generate substantial amounts of energy across the planet in its current capacity.
- Cleaner energy alternatives will gradually replace coal use because they present better environmental prospects.
Innovations in Coal Processing
- Scientists actively pursue developments of clean technologies for coal processing methods.
- The financial performance of technological solutions determines their adoption across wide areas.
Explore Our Premium Coal Solutions
Conclusion
The industrial advancement depends heavily on coal as it functions vital in electricity generation together with steel making and industrial processes. As one of the fundamental fuel sources coal keeps its central position while environmental issues in coal mining and processing ask for sustainable and responsible solutions.
As a reputable manufacturer and exporter Jay Ganesh Minerals delivers high-quality industrial fuel which provides reliable performance of Lignite Coal and Indonesian Coal for worldwide energy requirements. The company provides coal supplies designed for maximum performance to deliver premium-grade materials that power generation facilities and industries need. The company positions itself as an essential participant in delivering premium coal.









