
Industrial Coal Grades: Which is Best for Your Industry?
10 January, 2026
04 December, 2025
Coal remains one of the world’s most widely used industrial fuels, powering everything from power plants and cement kilns to paper mills and chemical industries. As industries evolve and energy requirements grow, choosing the right type of coal becomes essential for controlling costs, improving combustion efficiency, and minimizing environmental impact.
Among the most commonly used coal types in global industries today are Indonesia coal and lignite coal. Both have distinct physical, chemical, and economic characteristics, making them suitable for different applications. Understanding their energy content, cost-effectiveness, and industrial uses helps businesses make informed fuel decisions that align with operational goals.
This detailed comparison explores how both fuels differ covering heating value, moisture levels, price variations, availability, applications, and combustion performance.
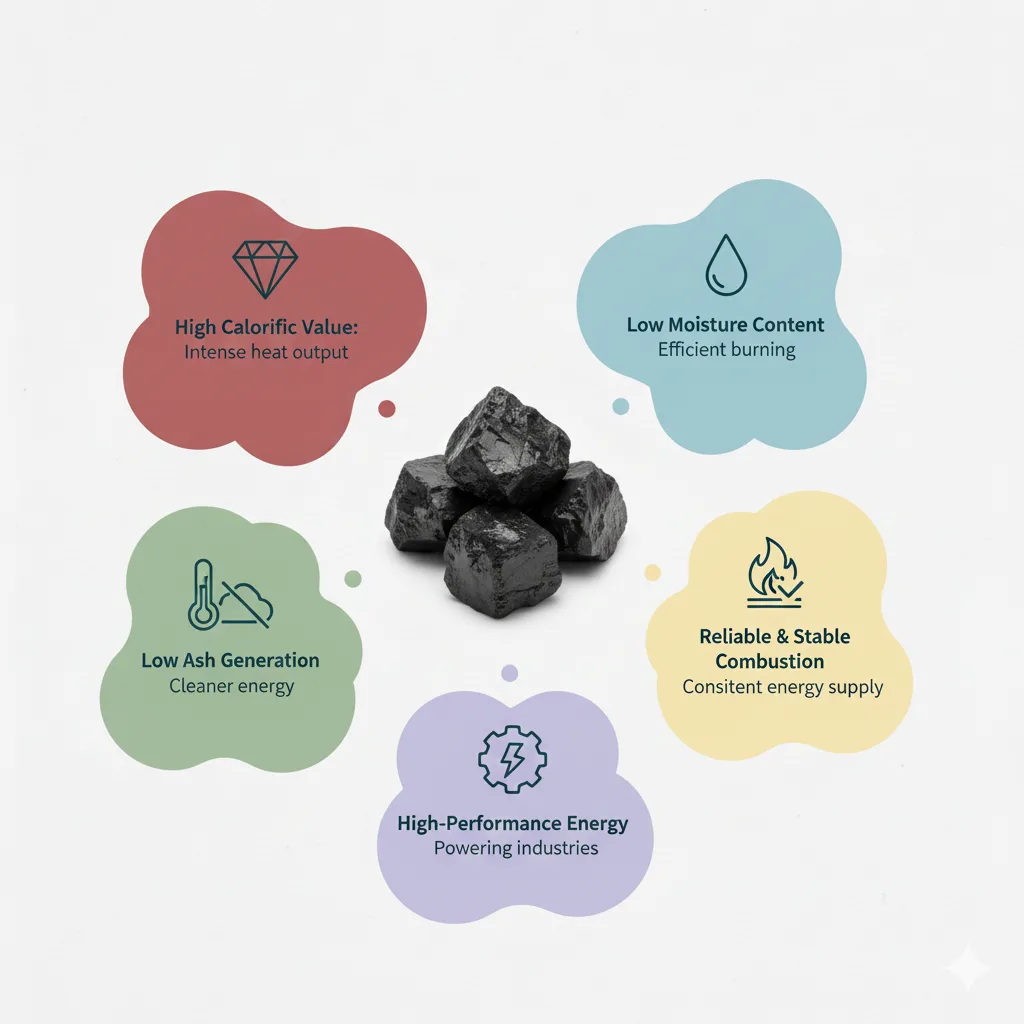
Indonesia coal is known worldwide for its high calorific value, low moisture content, and low sulfur and low ash composition. These properties make it one of the most efficient and clean-burning coal types available in international markets. Due to its premium combustion quality, Indonesia has become a leading exporter and a reliable Indonesia coal supplier for industries across Asia, Africa, and the Middle East.
High calorific value
Low moisture content
Low ash generation
Reliable and stable combustion
Suitable for high-performance energy applications
Its clean-burning characteristics also reduce emissions compared to high-moisture coals, supporting modern sustainability goals.
Lignite coal, also called brown coal, is an early geological stage of coal formation. It contains high moisture and high ash content, which naturally give it a lower calorific value and low carbon content compared to bituminous or Indonesian alternatives.
Though it offers lower energy per kilogram, lignite coal remains extremely popular because it is cost-effective, easily available in many regions, and ideal for industries requiring bulk fuel at a lower price point. For processes where consistent high heat is not mandatory, lignite coal provides a dependable and economical solution.
Lower calorific value
High ash and moisture
Reduced combustion efficiency
Affordable price compared to higher grades
Used primarily in local markets due to transportation cost sensitivity
Despite its lower coal heating value, its affordability makes it essential for power plants, brick manufacturing, gasification, fertilizer units, and industries where operating costs must remain minimal.
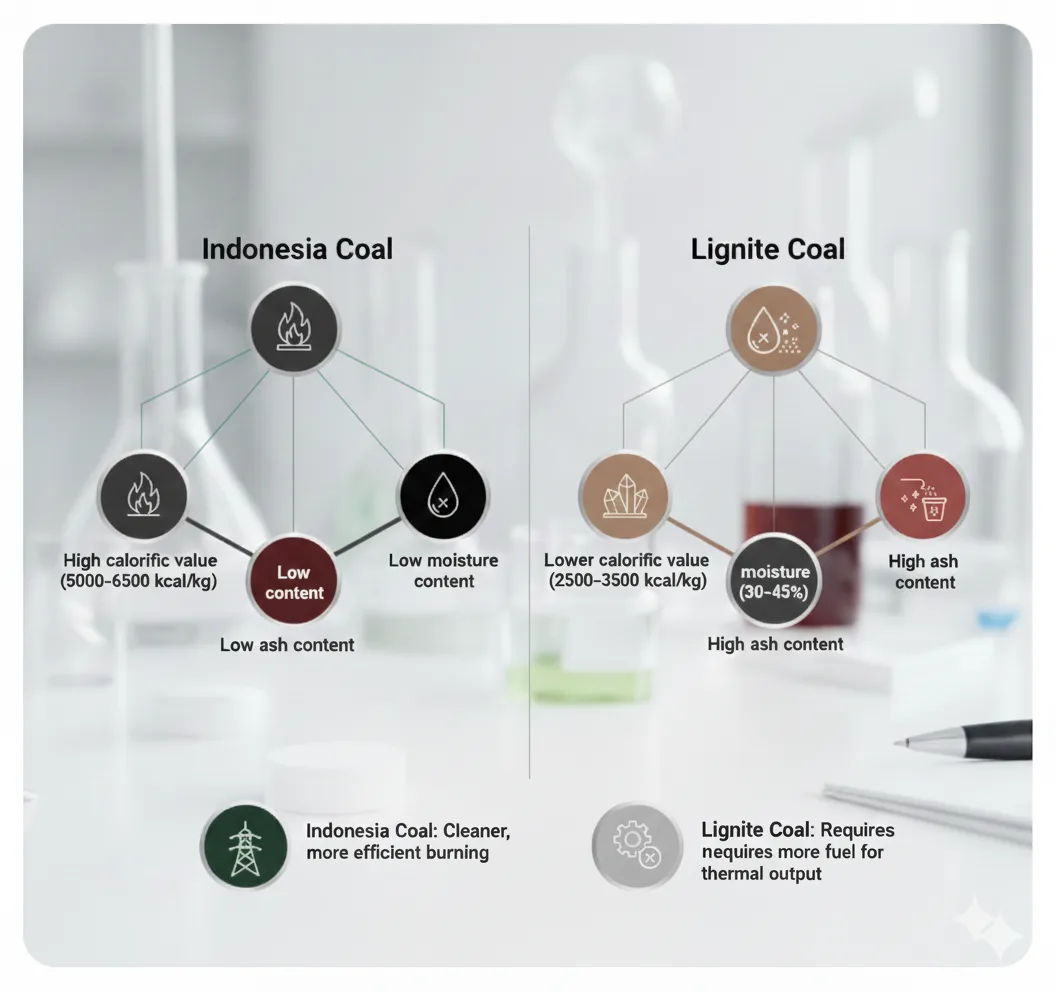
One of the most important differences lies in the coal energy content. Indonesia coal is considered a high calorific value coal, which means it delivers more heat per kilogram. This increases combustion efficiency and reduces fuel consumption in boilers and furnaces.
Indonesia Coal: 5000–6500 kcal/kg (high calorific value)
Lignite Coal: 2500–3500 kcal/kg (lower calorific value)
This significant difference directly affects process efficiency and energy output. Industries needing stronger heat generation prefer Indonesia coal for stable coal combustion.
Moisture and ash play a major role in overall boiler efficiency.
Indonesia Coal:
Low moisture content
Low ash content
Results in cleaner and more efficient burning
Lignite Coal:
High moisture (often 30–45%)
High ash content
Requires more fuel for the same thermal output
Thus, while lignite coal is cheaper, operational energy loss due to moisture and ash must be considered.
Indonesia coal burns efficiently with steady heat due to its high carbon and low-water composition. Lignite coal, due to high moisture, burns rapidly but with fluctuating temperature levels.
Applications requiring long, consistent heating loads naturally choose Indonesian grades for their reliability.
Coal prices vary significantly based on global demand, grade, transportation, and miner-to-industry supply chain conditions. Currently:
Indonesia coal price generally remains higher due to export-grade quality, superior combustion, and global demand.
Lignite coal price stays lower because of its local availability, lower calorific value, and higher moisture levels.
Fuel grade and calorific value
Global mining output
Shipping costs
Import/export duties
Moisture percentage
Industrial fuel demand cycles
If an industry values energy efficiency and reduced maintenance, Indonesia coal becomes more cost-effective despite its higher price. For industries seeking economical bulk energy, lignite remains a practical choice.
Coal for electricity generation: offers stable heat output, making it ideal for high-capacity thermal power plants requiring consistent performance.
Coal power generation in large industrial boilers: Ensures efficient combustion with less residue, reducing maintenance downtime.
Coal for power plants requiring high calorific value: Provides superior heating value, improving overall plant efficiency and energy yield.
Cement manufacturing: Delivers uniform heat essential for clinker formation and smoother kiln operation.
Paper mills: Supports continuous steam generation required for drying, pulping, and paper finishing processes.
Chemical and fertilizer industries: Provides controlled heat necessary for chemical reactions and synthesis processes.
Textile industries: Ensures clean combustion for dyeing, washing, and steam-related textile applications.
Metallurgical operations: Suitable for processes needing high temperature and consistent thermal energy.
Industrial boilers & heating systems: Reduces ash accumulation, providing cleaner heating cycles and enhanced boiler life.
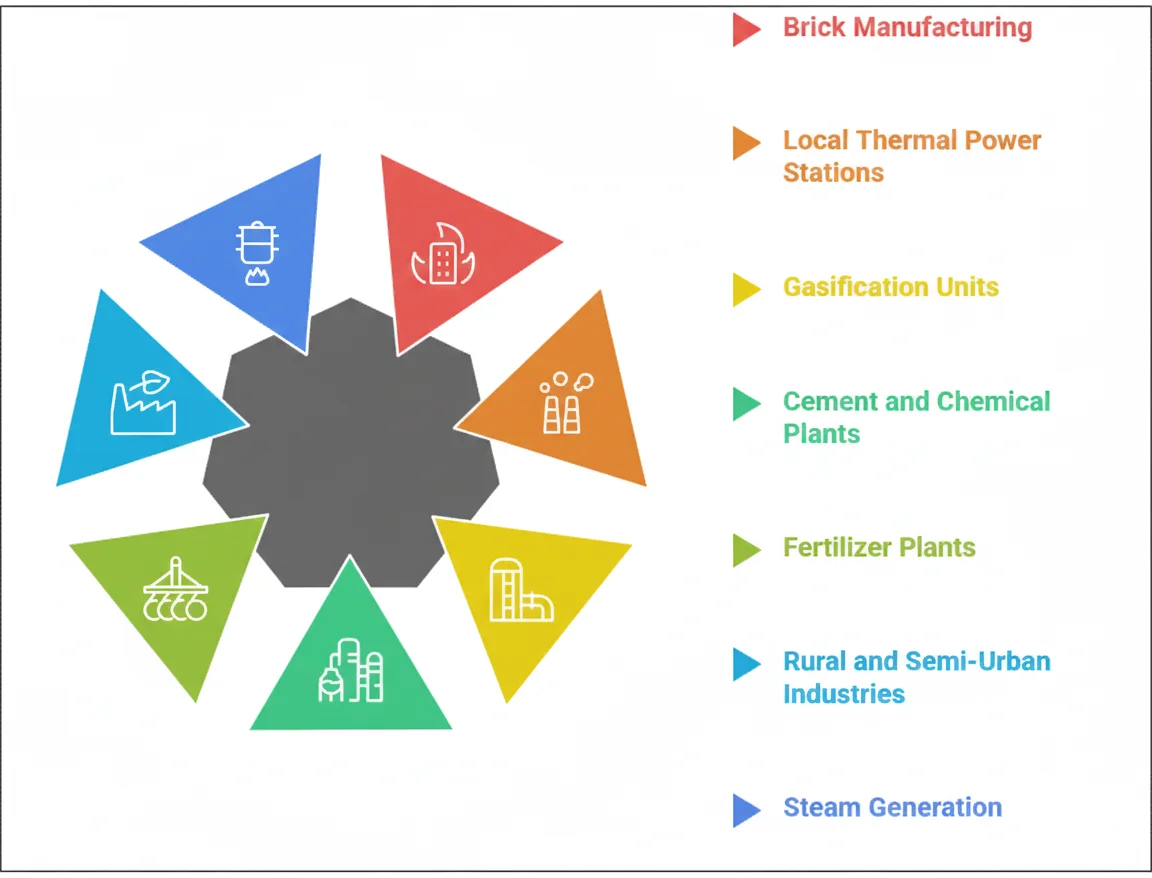
Brick manufacturing: Offers an economical heat source for firing bricks, keeping production costs low.
Local thermal power stations: Ideal for short-distance transport and low-cost electricity generation in regional grids.
Gasification units: Used to produce syngas, thanks to its affordability and easy availability.
Cement and chemical plants: Suitable for operations where moderate heat is sufficient for process completion.
Fertilizer plants: Provides an affordable energy solution for generating process steam and heat.
Rural and semi-urban industries: Cost-effective fuel option for local industries with high volume but low heat needs.
Steam generation for smaller setups: Works well for low-pressure boilers used in small manufacturing units.
| Feature | Indonesia Coal | Lignite Coal |
|---|---|---|
| Calorific Value | High calorific value coal (5000–6500 kcal/kg) | Lower calorific value (2500–3500 kcal/kg) |
| Moisture Content | Low moisture content | High moisture (30–45%) |
| Ash Content | Low ash | High ash content |
| Carbon Content | Moderate to high | Low carbon content |
| Combustion Efficiency | Strong, stable heat | Moderate, fluctuating heat |
| Price | Higher Indonesia coal price | Lower lignite coal price |
| Industrial Use | Power plants, cement, paper, chemicals | Bricks, fertilizers, low-budget power plants |
| Environmental Impact | Lower emissions | Higher emissions due to ash & moisture |
Choose Indonesia Coal if you need superior heat efficiency: Its high calorific value reduces fuel consumption and delivers stronger, more stable thermal output.
Choose Indonesia Coal for cleaner operations: Low moisture and ash content help maintain boilers, reduce emissions, and improve burning efficiency.
Choose Indonesia Coal for energy-critical industries: Ideal for cement, chemicals, paper, and power plants requiring uninterrupted high-temperature performance.
Choose Lignite Coal if your priority is low-cost bulk fuel: It is budget-friendly and meets the needs of industries that operate on large fuel volumes.
Choose Lignite Coal for moderate heat applications: Perfect for bricks, fertilizers, and smaller power units that do not demand high heat.
Choose Lignite Coal if fuel availability matters more than calorific value: Often available locally, reducing transportation and logistical expenses.
Choose mixed-usage strategies for flexible operations: Many industries blend Indonesia and lignite coal to optimize cost versus energy output across seasons.
Jay Ganesh Minerals has established itself as a trusted partner for industries seeking consistent-quality Indonesia coal and lignite coal. With strong sourcing capabilities, quality-driven processing, and professional logistics, the company ensures timely delivery to clients across diverse industrial sectors.
Their industry expertise, commitment to quality, and customer-focused service make them a preferred choice for businesses seeking reliable coal supply whether for high-calorific-value applications or cost-efficient energy solutions.
Both Indonesia coal and lignite coal play essential roles in industrial energy today. While Indonesian grades deliver superior energy content, cleaner burning, and higher efficiency, lignite coal remains an economical option for industries focusing on cost over performance. Understanding the differences in ash, moisture, calorific value, and price helps companies make smarter energy decisions.
By evaluating your energy needs carefully and partnering with a trusted supplier like Jay Ganesh Minerals, you can ensure reliable, efficient, and cost-effective fuel for your operations.
Indonesia coal has significantly higher calorific value, making it more energy-dense and efficient than lignite coal. Its lower moisture and ash contribute to stronger heat output and better combustion.
Moisture levels, ash percentage, calorific value, and carbon content create distinct differences between coal types. These characteristics determine combustion efficiency and suitable industrial applications.
Yes, lignite coal is widely used in local thermal power plants where cost-efficiency is more important than maximum heat generation. However, it delivers lower energy output than higher-grade coals.
Due to its high calorific value, lower moisture, and stable combustion performance, Indonesia coal ensures higher efficiency, reduced emissions, and lower maintenance costs.
Export policies, shipping costs, global fuel demand, mining output, and calorific value directly influence coal price fluctuations.

Whatsapp Chatx
Hi! Click one of our representatives below to chat on WhatsApp or send us email to [email protected]

|
Mr. RAJESH +91 99130 87000 |

|
Mr. JIGNESH +91 89800 70055 |

