
Industrial Coal Grades: Which is Best for Your Industry?
10 January, 2026
03 December, 2025
Industrial mineral form the backbone of countless industries from ceramics and refractories to electronics, metallurgy, casting, and advanced engineering. Among these, Zirconium Silicate and Alumina stand out as two high-performance minerals trusted globally for their unique properties and ability to withstand extreme industrial conditions.
Though both minerals appear similar in their thermal and structural behavior, their performance, cost, applications, and chemical characteristics vary significantly. This detailed comparison helps manufacturers, engineers, and procurement professionals make informed decisions based on real-world industrial requirements.

Zirconium Silicate (ZrSiO₄) is a naturally occurring mineral derived from zircon-rich sands. Known for its excellent thermal stability, chemical inertness, and resistance to high-temperature environments, it is widely used in industries that require purity, durability, and structural performance.
At Jay Ganesh Minerals, Zirconium Silicate is sourced from high-quality deposits and processed under strict quality controls to maintain consistency across every batch.
High thermal stability: Performs exceptionally under extreme temperatures without structural deformation.
Chemical inertness: Highly resistant to acids, alkalis, and corrosive materials.
Low thermal expansion: Ensures dimensional accuracy in high-temperature applications.
Good hardness & durability: Suitable for precision casting and wear-resistant applications.
High resistance to radiation: Widely used in nuclear and high-energy environments.
Low electrical conductivity: Ideal for ceramics and insulating materials.
Because of these zirconium silicate properties it is widely used in ceramics, tile glazes, sanitaryware, precision casting, and refractory coatings.
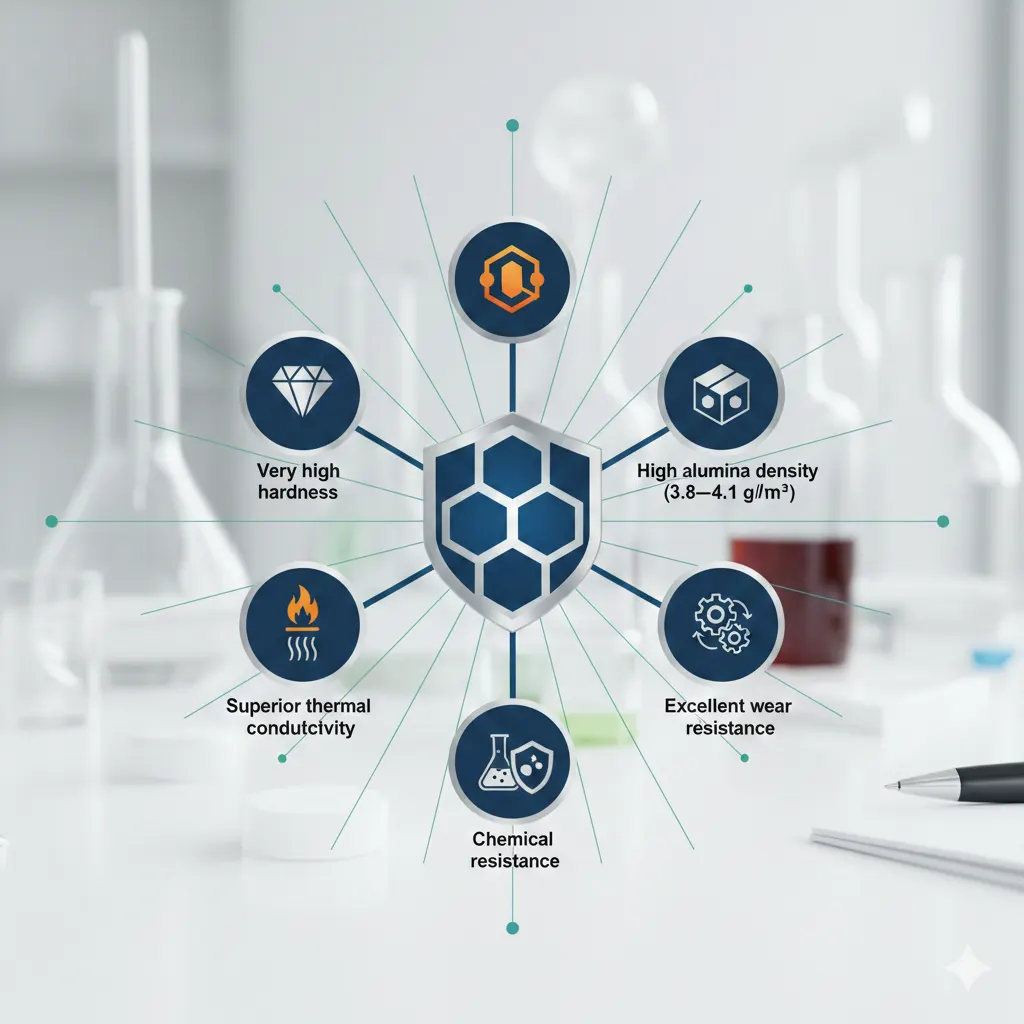
Alumina (Al₂O₃), or aluminum oxide, is one of the most widely used industrial minerals across engineering, thermal, electronic, and refractory applications. With a combination of superior hardness, high alumina density, and excellent alumina thermal conductivity, it is a prime material for industries that demand extreme strength and heat resistance.
Very high hardness: One of the hardest industrial minerals, close to diamond on the Mohs scale.
High alumina density (3.8–4.1 g/cm³): Ensures strength under mechanical load.
Superior thermal conductivity: Essential for heat dissipation in electronics and high-temperature systems.
Excellent wear resistance: Perfect for abrasives, grinding media, and cutting tools.
High heat stability (up to 2000°C+): Widely used in refractories and furnace linings.
Chemical resistance: Stable in harsh industrial environments.
Its high-performance characteristics make Alumina critical in refractories, abrasives, electronics, thermal systems, and advanced ceramics.
Below is a comprehensive table comparing both minerals based on key industrial performance parameters:
| Parameter | Zirconium Silicate (ZrSiO₄) | Alumina (Al₂O₃) | Which Is Better? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density | 4.5–4.6 g/cm³ | 3.8–4.1 g/cm³ | Zirconium Silicate |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent | Excellent | Tie |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low | High | Alumina |
| Chemical Inertness | Very High | High | Zirconium Silicate |
| Melting Point | ~2550°C | ~2050°C | Zirconium Silicate |
| Hardness | Medium–High | Very High | Alumina |
| Electrical Conductivity | Very Low | Low | Zirconium Silicate |
| Major Industrial Applications | Ceramics, Glazes, Casting, Refractories | Refractories, Abrasives, Electronics | Depends on Use-Case |
Zirconium Silicate shines in extreme heat environments thanks to its ability to retain physical and chemical stability even at temperatures exceeding 1500°C.
Withstands thermal shock
Stable in aggressive atmospheres
Ideal for zircon-based refractory coatings
Enhances glaze opacity in tiles and sanitaryware
Maintains whiteness under heat
Its chemical resistance makes it especially valuable in industries dealing with molten metals, corrosive compounds, and high-temperature ceramics.
Alumina is known for its unmatched combination of hardness, heat resistance, and mechanical strength.
Handles heavy thermal load
Crucial for furnace linings, kiln furniture, and burner blocks
High alumina thermal conductivity improves heat transfer
Withstands rapid temperature fluctuations
Superior wear resistance for grinding and abrasive applications
In industries where friction, mechanical stress, or rapid heating occurs, Alumina is often the preferred choice.
Outstanding resistance to acids
Resistant to molten metals
Highly inert in aggressive chemical environments
Very good resistance to most chemicals
Can be attacked by some fluxes and strong alkalis
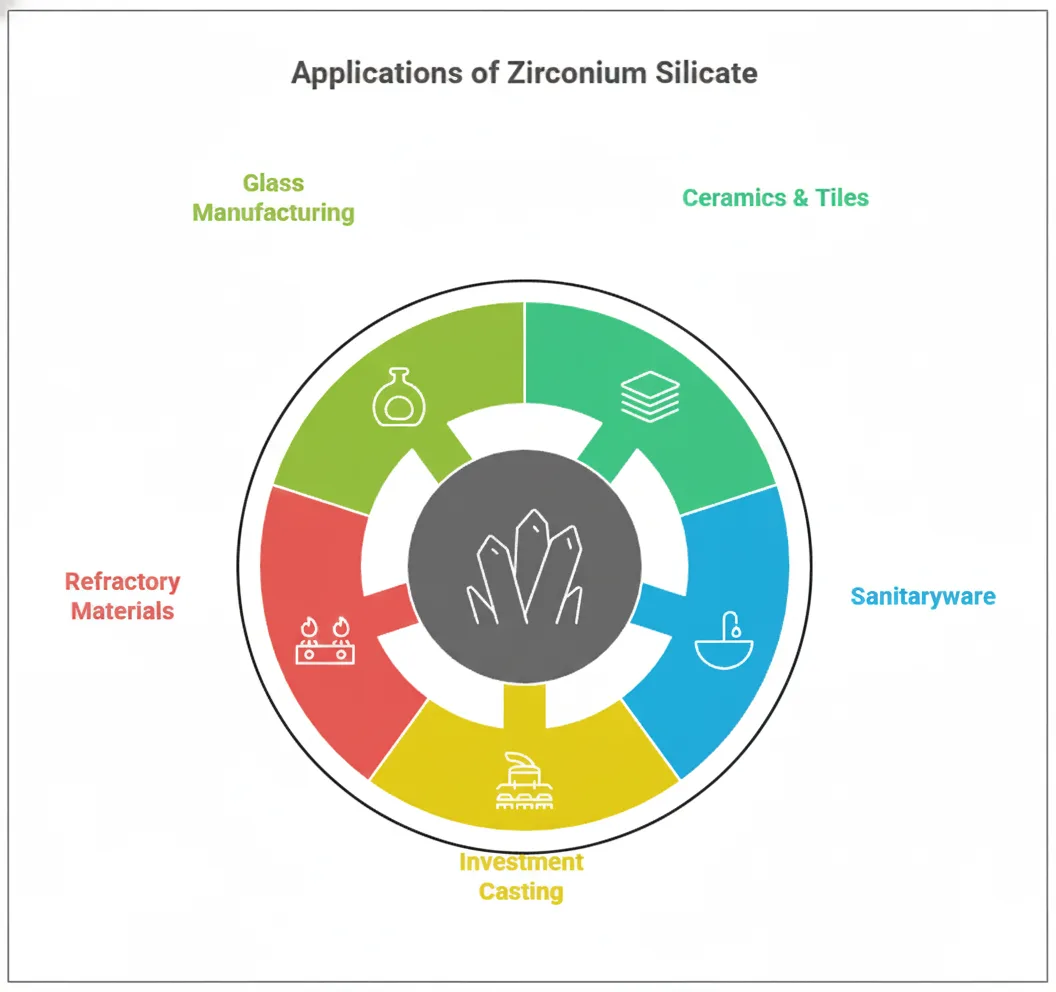
Zirconium Silicate plays a crucial role in industries requiring precision, whiteness, and thermal stability.
Used as an opacifier to improve gloss, whiteness, and surface finish.
Ensures strength, smoothness, and thermal performance.
Ideal for shells, molds, and precision castings.
Provides high thermal stability and resistance to molten metals.
Improves transparency, chemical durability, and melting performance.
Jay Ganesh Minerals ensures consistent particle size, purity, and processing for all ceramic and refractory applications.
Alumina is critical in industries that require extreme hardness and high thermal performance.
Used in firebricks, castables, furnace linings, and kiln equipment.
Used in polishing wheels, cutting tools, and industrial abrasives.
Used for insulating substrates and heat dissipation materials.
Used as a flux and structural component for high-temperature operations.
Used in spark plugs, ceramic bearings, seals, and precision components.
Excellent thermal shock resistance
Superior chemical inertness
Ideal for coatings and precision molds
Withstands extremely high temperatures
Superior mechanical strength
Perfect for furnace linings and bulk refractory construction
Use Zirconium Silicate for coatings, glazes, and precision casting.
Use Alumina for heavy-duty, load-bearing, high-temperature zones.
Your selection should depend on:
Operating temperature
Chemical environment
Required mechanical strength
Thermal conductivity needs
Cost and sourcing availability
Application type (coating, structural, refractory, electronic, abrasive)
Both minerals offer industry-leading performance but they serve different purposes based on operational demands.
Jay Ganesh Minerals is a trusted global supplier of high-purity Zirconium Silicate. With strict quality control, consistent processing, and reliable logistics, the company ensures every batch meets the demanding needs of ceramics, tiles, sanitaryware, foundries, and refractories.
Sourcing from high-quality zircon deposits
Consistent particle size and chemical purity
Advanced processing & reliable supply chain
Serving global ceramic, glass, and refractory industries
Delivering bulk quantities with assured quality
Our commitment to quality has earned the trust of manufacturers across multiple countries and industries.
Explore Mineral Property Differences
Zirconium Silicate and Alumina are both high-performance industrial minerals, but they excel in different domains. Zirconium Silicate offers remarkable chemical inertness, higher melting point, and stability for ceramics and precision casting, while Alumina provides outstanding hardness, wear resistance, and thermal conductivity for advanced engineering, refractories, and electronics.
Choosing the right mineral depends on your industrial needs and with expert guidance and consistent quality, Jay Ganesh Minerals ensures you make the right choice for every application.
Both perform well, but Zirconium Silicate offers better chemical resistance and a higher melting point.
Alumina is significantly harder, making it ideal for abrasives and cutting applications.
Its melting point is approximately 2550°C, making it extremely stable for industrial heat applications.
Alumina is generally more economical, but Zirconium Silicate delivers better performance in chemical and ceramic applications.

Whatsapp Chatx
Hi! Click one of our representatives below to chat on WhatsApp or send us email to [email protected]

|
Mr. RAJESH +91 99130 87000 |

|
Mr. JIGNESH +91 89800 70055 |

