
HS Code for Industrial Mineral & Clay: Export - Import Guide
04 February, 2026
01 December, 2025
Processed clay plays an essential role in shaping some of the world’s most important industries from ceramics and construction to agriculture, cosmetics, and drilling. With its natural plasticity, absorbent properties, mineral-rich composition, and high heat resistance, processed clay has become a core ingredient in products and industrial applications across global markets.
As one of the trusted clay manufacturers in India, Jay Ganesh Minerals supplies high-grade processed clay that meets international quality standards. This blog explores the top 10 industrial uses of processed clay, the properties that make it so valuable, and why industries depend on this mineral every single day.
Processed clay is a refined form of natural clay that undergoes a series of steps mining, crushing, drying, grinding, and sometimes purification to meet industrial-quality requirements. Unlike raw clay, which may contain impurities, processed clay is uniform in texture, consistent in quality, and suitable for specialized manufacturing.
The production process involves:
Mining: Clay is extracted from high-quality deposits.
Drying: Moisture is reduced to stabilize the material.
Grinding & Sieving: The clay is broken down into fine particles.
Purifying: Removal of impurities improves performance.
Grading: The clay is classified based on industrial needs.
After processing, the clay becomes suitable for applications that require specific chemical or physical characteristics such as heat resistance, plasticity, density, absorption, or filtration capacity.

Different industries require different forms of refined clay, including:
Ceramic clay: for tiles, sanitaryware, and porcelain.
Pottery clay: for handicrafts and artistic applications.
Brick making clay: for bricks clay and tiles clay industries.
Refractory clay: for high-temperature furnaces.
Construction clay: for soil stabilization and geotechnical work.
Cosmetic clay: for skincare and wellness applications.
Soil conditioning clay: for agricultural enhancement.
With these properties and classifications, processed clay becomes a versatile industrial mineral used across the world.
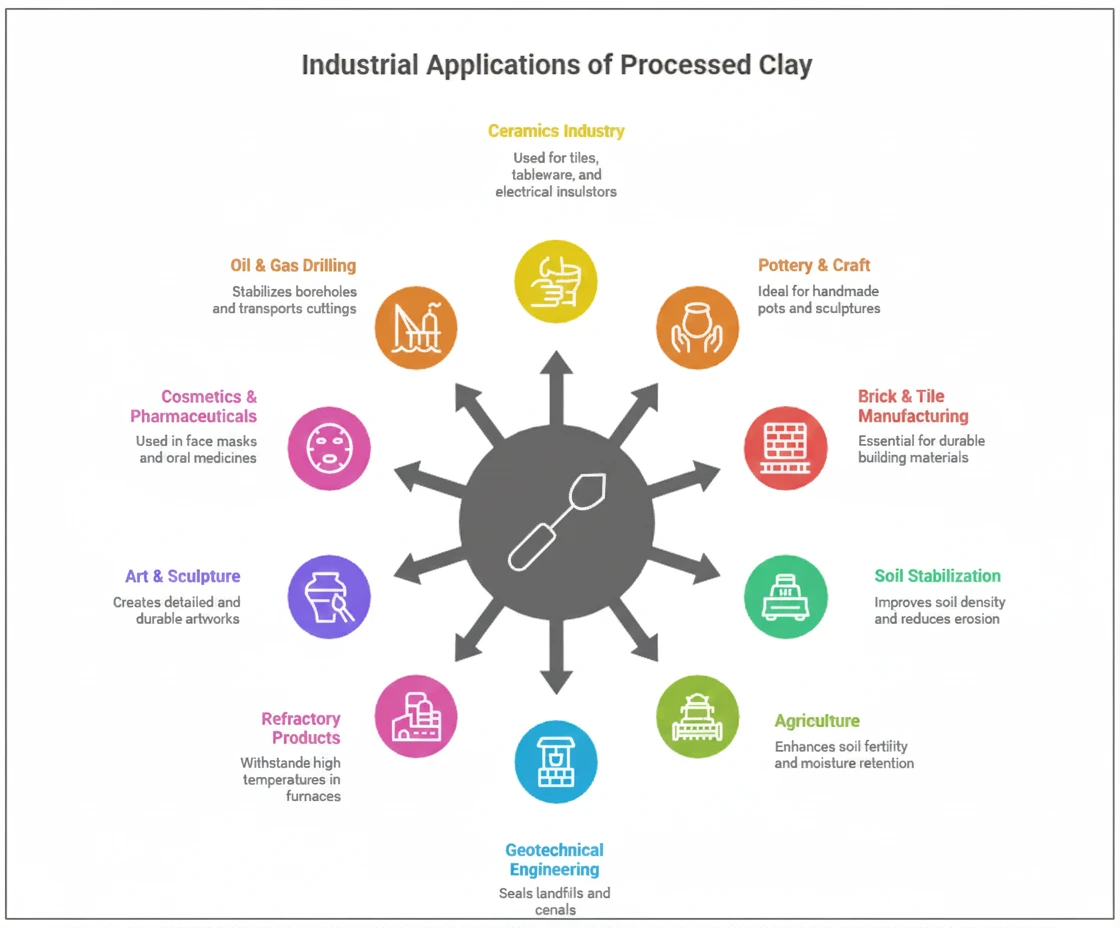
Below are the top 10 applications that demonstrate the industrial importance of processed clay.
Each point includes a detailed explanation not short summaries to ensure deep value and strong SEO performance.
The ceramics sector is one of the largest consumers of processed clay, especially ceramic clay known for its exceptional plasticity, fine texture, and ability to withstand high firing temperatures. Ceramic manufacturers use processed clay to produce:
Ceramic tiles: Processed clay provides a smooth, durable base for floor and wall tiles.
Porcelain tableware: Ensures high density and strength needed for premium dining products.
Sanitaryware: Gives toilets, basins, and bathroom fittings the required hardness and finish.
Electrical porcelain: Used to create insulators with excellent thermal and electrical resistance.
Decorative ceramics: Allows fine detailing and glazing for artistic ceramic pieces.
The clay’s natural mineral structure helps ceramic products maintain shape during firing while enhancing strength and durability. The consistency of processed clay allows manufacturers to create detailed designs, smooth surfaces, and high-quality finishes. For the ceramics industry, processed clay isn’t just an ingredient it is the foundation of the entire manufacturing process.
Another significant use of processed clay is in pottery, where artisans and commercial manufacturers rely on pottery clay for its moldability and aesthetic properties. Pottery requires clay that responds well to shaping, carving, and handwork.
Processed clay is used to make:
Handmade pots: Offers perfect plasticity for shaping traditional and modern pottery.
Art sculptures: Provides a stable material for detailed sculptural work without cracking.
Terracotta décor: Creates long-lasting artistic pieces with natural earthy texture.
Craft accessories: Used for small artifacts due to its moldability and uniform drying.
Studio pottery: Supports high-quality, consistent clay bodies used by professional potters.
Because processed clay has refined particle size and uniform moisture content, it is easier for craftsmen to shape the product without cracks or deformities. Whether for mass production or artisan-level studio work, pottery clay offers creative freedom and consistent performance, making it indispensable for the craft industry.
The construction industry depends heavily on brick making clay, bricks clay, and tiles clay to manufacture durable, high-strength building materials. Processed clay improves the physical properties of bricks and tiles by offering:
Clay bricks: Ensures strong, dimensionally stable bricks for building construction.
Roofing tiles: Provides weather resistance and firing strength for roof tile production.
Paver tiles: Creates heavy-duty surface tiles capable of withstanding high foot traffic.
Hollow blocks: Enhances thermal insulation and reduces block weight.
Facing bricks: Used to produce smooth, attractive front-facing architectural bricks.
From roofing tiles to wall bricks, processed clay ensures the finished products can endure harsh environments, thermal changes, and heavy loads. The modern demand for lightweight yet durable construction materials has also increased the use of processed clay in advanced tile and paver manufacturing.
Clay plays a vital role in geotechnical engineering and civil infrastructure projects. Construction clay is used to stabilize soil, especially in areas where the ground lacks structural strength.
Its swelling, binding, and compaction properties improve:
Road base layers: Clay improves soil density and strengthens subgrade layers.
Foundation support: Reduces soil movement and increases load-bearing capacity.
Building embankments: Helps form compact, stable slopes in infrastructure projects.
Drainage control: Reduces soil permeability to manage water movement.
Slope stabilization: Acts as a binding agent to prevent soil erosion on slopes.
Processed clay reduces soil permeability, which helps prevent water seepage and erosion. Its use in large-scale infrastructure projects such as highways, industrial parks, and pipelines makes it a crucial material in modern construction.
Processed clay also serves as an important agricultural resource. Agricultural clay and soil conditioning clay are used to enhance soil fertility and improve the physical properties of farmland.
Key benefits include:
Moisture retention: Helps sandy soils hold water for longer periods during drought.
Nutrient binding: Enhances the soil’s ability to retain fertilizers and micronutrients.
Root development: Promotes better aeration and structure for stronger plant roots.
Soil improvement mixes: Used in potting mixes to balance texture and fertility.
Erosion prevention: Creates stable topsoil that resists wind and water erosion.
In sandy soils, clay helps improve moisture levels, creating a healthier environment for plants. In horticulture and nursery applications, clay-rich soil mixtures promote stronger root development. Its natural mineral content makes clay an eco-friendly and cost-effective solution for agricultural improvement.
In geotechnical applications, processed clay especially bentonite-based clay is used as a sealing and lining material. Its ability to expand when hydrated makes it ideal for engineering projects requiring natural sealing.
Common uses include:
Landfill liners: Forms impermeable barriers to prevent leachate contamination.
Canal sealing: Stops seepage and water loss in irrigation canals and reservoirs.
Borehole sealing: Fills gaps around wells to prevent groundwater contamination.
Groundwater barriers: Helps isolate polluted zones from clean aquifers.
Tunnel backfilling: Provides structural support and reduces water ingress in tunnels.
Because clay naturally prevents seepage, it is widely used to contain contaminants, manage water flow, and stabilize underground structures. Its performance reliability makes clay a preferred material for engineering consultants and construction companies involved in environmental and infrastructure projects.
Industries that operate at extremely high temperatures rely on refractory clay and heat resistant clay to manufacture materials that can withstand thermal shock and intense heat.
These industries include:
Fire bricks: Withstands extreme furnace temperatures without structural failure.
Kiln linings: Provides insulation and protection for high-temperature kilns.
Crucibles: Enables safe melting and handling of metals and alloys.
Thermal boards: Used as heat shields and insulation panels in industrial furnaces
Boiler linings: Resists chemical and thermal attack inside boilers and reactors.
Processed clay with high alumina and silica content is used to make fire bricks, refractory linings, and insulating boards. These materials maintain structural integrity even under continuous exposure to temperatures exceeding 1400°C. This makes refractory clay one of the most critical materials in heavy manufacturing industries.
Artists and sculptors have long used clay as a medium to create lifelike forms and intricate designs. Processed clay used in sculpture is valued for its smooth texture, pliability, and minimal cracking.
Applications include:
Terracotta statues: Offers excellent shaping ability for detailed artistry.
Architectural murals: Forms durable decorative panels for exterior and interior design.
Miniature models: Supports delicate work with fine detailing and smooth finishes.
Large installations: Provides structural strength for big artistic structures.
Museum replicas: Ensures accurate reproduction of historical artifacts.
The uniformity of refined clay ensures better detailing and long-lasting durability of artistic creations. For fine arts, processed clay remains unmatched in versatility and creative potential.
One of the fastest-growing applications of processed clay is in the cosmetics and pharmaceutical industry. Cosmetic clay such as kaolin and bentonite is used for its ability to absorb impurities, detoxify skin, and enhance product texture.
Uses include:
Face masks: Removes impurities and excess oil from the skin naturally
Cleansing powders: Acts as a gentle exfoliant suitable for sensitive skin.
Detox formulations: Binds toxins and heavy metals in wellness products.
Topical ointments: Provides soothing, anti-inflammatory properties for skincare.
Oral medicines: Works as a safe binding and stabilizing agent in pharmaceuticals.
Processed clay helps control oil, remove toxins, and soothe skin irritations. In the pharmaceutical industry, clay is used as a binding agent, detoxifier, and absorbent in oral medications. This combination of purity, safety, and effectiveness makes processed clay a valuable ingredient in wellness products.
The oil and gas drilling industry is one of the largest users of bentonite-rich processed clay. In drilling operations, processed clay is used to make drilling mud, which plays multiple roles:
Drilling mud: Stabilizes boreholes and maintains pressure during drilling operations.
Lubrication fluid: Reduces friction on the drill bit for smoother penetration.
Cuttings transport: Carries rock cuttings to the surface efficiently.
Wellbore sealing: Prevents fluid loss and maintains structural integrity of the well.
Pressure control: Helps balance downhole pressure to prevent blowouts.
Without processed clay, modern deep-drilling operations would face structural challenges and significant safety risks. Its natural swelling and gel-forming properties make it essential for efficient drilling.
Industries choose processed clay because of its several advantages:
Improved manufacturing quality
High-temperature resistance
Excellent absorbency
Natural environmental compatibility
Cost-effective industrial material
Long-lasting structural support
Because of these benefits, processed clay continues to be a preferred material across multiple sectors.
Jay Ganesh Minerals is known for delivering consistently high-quality processed clay that meets international standards. We provide:
Premium-grade refined clay
Strict quality control and mineral purity
Custom grading for industrial applications
Reliable supply capacity
Export-quality processed clay for global markets
Our expertise and mining experience make us one of India’s trusted suppliers for industries using processed clay.
Processed clay is a powerful industrial resource with applications that impact everyday life from buildings and art to agriculture, energy, and personal care. Its adaptability and natural properties make it one of the most valuable minerals in the modern world.
With decades of experience, Jay Ganesh Minerals continues to supply high-quality processed clay solutions tailored to the growing needs of global industries. Whether you require ceramic clay, bricks clay, refractory clay, or agricultural clay, our refined products ensure consistency, performance, and long-term value.
Processed clay is used in ceramics, pottery, bricks, tiles, soil stabilization, agriculture, geotechnical projects, refractories, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and oil & gas drilling.
It improves soil stability, reduces permeability, and enhances load-bearing capacity, making it essential for roads, foundations, and infrastructure projects.
Yes. Cosmetic clay is purified and refined to remove impurities, making it safe for skin applications.
Brick manufacturing, tile production, ceramics, drilling, and refractory industries are among the largest consumers.

Whatsapp Chatx
Hi! Click one of our representatives below to chat on WhatsApp or send us email to [email protected]

|
Mr. RAJESH +91 99130 87000 |

|
Mr. JIGNESH +91 89800 70055 |

